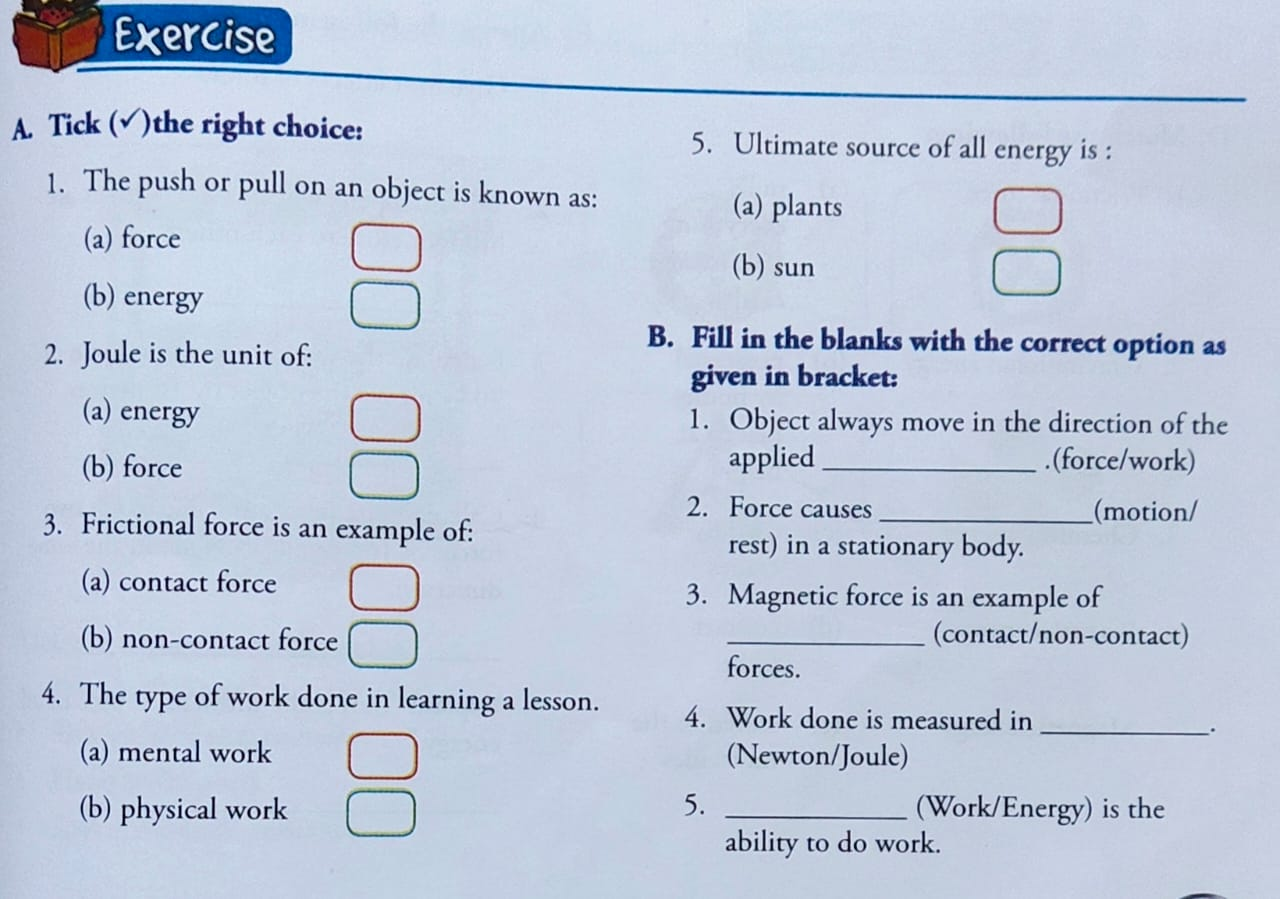
A. Tick the right choice:
1. Answer- (a) Force
2. Answer- (a) Energy
3. Answer- (a)Contact Force
4. Answer- (a) Mental work
5. Answer- (b) Sun
1. Answer- (a) Force
2. Answer- (a) Energy
3. Answer- (a)Contact Force
4. Answer- (a) Mental work
5. Answer- (b) Sun
B. Fill in the blanks with the correct option as given in bracket:
1. Answer- Force
2. Answer- motion
3. Answer- non-contact
4. Answer- joule
5. Answer- Energy
1. Answer- Force
2. Answer- motion
3. Answer- non-contact
4. Answer- joule
5. Answer- Energy
C. Write true or false:
1. Answer- False
2. Answer- True
3. Answer- True
4. Answer- False
5. Answer- False
1. Answer- False
2. Answer- True
3. Answer- True
4. Answer- False
5. Answer- False
D. Match the following:
Answer-
Answer-
1. Frictional force (d) Contact force
2. Gravitational energy (a) pull everything towards the earth
3. Chemical energy (e) Stored in the molecules
4. Potential energy (b) Possessed by bodies placed at height
5. Magnetic energy (c) Used by cranes.
2. Gravitational energy (a) pull everything towards the earth
3. Chemical energy (e) Stored in the molecules
4. Potential energy (b) Possessed by bodies placed at height
5. Magnetic energy (c) Used by cranes.
F. Answer the following questions:
1. Give four effects of force.
Answer- The four effects of force are-
(i) Force causes motion in a stationary body.
(ii) Force can stop a moving body.
(iii) Force can produce a change in speed.
(iv) Force can change the direction of motion of a body.
1. Give four effects of force.
Answer- The four effects of force are-
(i) Force causes motion in a stationary body.
(ii) Force can stop a moving body.
(iii) Force can produce a change in speed.
(iv) Force can change the direction of motion of a body.
2. What happens when two like poles are brought close to each other?
Answer- When like poles are brought close to each other. A strong push repel the both poles each other.
Answer- When like poles are brought close to each other. A strong push repel the both poles each other.
3. Calculate the work done when force of 70 N moves the object by 16 metres.
Answer- Force applied = 70 N
Distance = 16m
Work done =?
Formula to be used, Work done = Force x Distance
= 70 N x 16 m
= 1120 joule.
4. Calculate the resultant force when two forces of 16 N and 34 N acts in the same direction.
Answer- F1 = 16 N
F2 = 34 N
For the same direction, Resultant force = F1 + F2
= 16 N + 34 N = 50 N.
5. Explain, “Sun is the ultimate source of all energy.”
Answer- Sun is the ultimate source of all energy on the earth. Sun’s energy is taken by green plants to prepare their food. The green plants are eaten by herbivores and herbivores are further eaten by carnivores. In this way energy gets transferred to their body to one another.
= 1120 joule.
4. Calculate the resultant force when two forces of 16 N and 34 N acts in the same direction.
Answer- F1 = 16 N
F2 = 34 N
For the same direction, Resultant force = F1 + F2
= 16 N + 34 N = 50 N.
5. Explain, “Sun is the ultimate source of all energy.”
Answer- Sun is the ultimate source of all energy on the earth. Sun’s energy is taken by green plants to prepare their food. The green plants are eaten by herbivores and herbivores are further eaten by carnivores. In this way energy gets transferred to their body to one another.
Chapter - 10
4 . Why Solar eclipse should not be seen with naked eyes?
Light and Shadow
Ex - F Answer the following questions :-
Page - 111
1. Give three features of light.
Ans. - Three features of light are as follows :-
a) Light produces sensation of vision.
b) It travels in a straight line.
c) It can be reflected as well as refracted.
2. What is reflection?
Ans. - The bouncing back of light is known as reflection.
3. Differentiate between transparent and translucent objects.
Ans. - Transparent objects are the objects which allow light to pass through it.
Whereas, the objects which allow partial amount of light to pass through it are known as translucent objects.
Ans. - Solar eclipse should not be seen with naked eyes because direct rays of the sun can be harmful for our eyes.
Chapter - 9
Soil
Ex - G Answer the following questions :-
Page - 100
1. What is soil?
Ans.- A complex mixture of fine powder obtained by weathering of rocks, organic matter and Minerals is known as soil.
Ans.- Loamy soil is best for growing crops because it contains right amount of water, air and Minerals in it.
3. What do you understand by soil erosion?
Ans.- Soil erosion is the process of removal of fertile topsoil by the action of wind and water.
4. Give any two methods to conserve soil.
Ans.- Two methods to conserve soil are as follows :-
a) By terrace farming.
b) By growing grass and trees.
5. What is crop rotation?
Ans.- Crop rotation is the practice of planting different types of crops on the same field by which the soil recover's the minerals and nutrients that the previous crop has used.
Chapter - 8
Molecules and their Arrangement
Ex - G Answer the following questions :-
Page - 91
1. What is freezing ?
Ans. Freezing is the process in which liquid turns into solid on cooling.
2. What is the difference between evaporation and boiling?
Ans. Evaporation is a process in which substance changes to Vapour at normal temperature.
Whereas, boiling is a process which occurs when a substance is heated to a very high temperature so that it turns into vapour.
3. Give two characteristics of gases?
Ans. Two characteristics of gases are as follows :-
a) Gases do not have a fixed shape.
b) They have low density.
4. What is condensation?
Ans. - Condensation is a process in which liquid droplets are formed from vapour.
5. How is the change in state of matter is brought about?
Ans. The change in state of matter is brought about by application of heat.
Chapter - 7
States of Matter
1) What is matter?
Ans. Matter is any substance that occupies space and has mass.
Ans. Matter is any substance that occupies space and has mass.
2) Differentiate between the three states of matter.
Ans :-
Solids :-
1) Solids have a fixed shape and don't flow.
2) It occupies a definite volume and cannot be compressed.
3) In solids the molecules are strongly attracted towards each other and hence they are dense.
Liquids :-
1) Liquids do not have a fixed shape and can flow easily.
2) Liquids have an indefinite shape but definite volume and can be compressed slightly.
3) In liquids the molecules are not attracted towards each other with strong forces as in solids. Hence, they are less dense.
Gases :-
1) Gases do not have any shape of their own and take the shape of the container they are put in. Also, gases can flow easily.
2) They don't have a definite volume and can be compressed easily.
3) In gases, molecules are very weakly attracted towards each other. Hence, they are less dense.
3) What is an element? Give an example.
Ans. An element is the substance that is made - up of only one kind of atom.
Example - Hydrogen.
4) How is a compound different from a mixture?
Ans. A compound is the substance which is made - up of more than one kind of atoms and are combined together. Example - water (contains Hydrogen and Oxygen) .
Whereas, a mixture is the substance which is made up of more than one kind of atom but are not combined together. Example :- Mixture of water and salt.
5) What is evaporation and sublimation?
Ans. Evaporation is the process of conversion of liquid into vapour.
Sublimation is the process in which solid gets converted to gaseous form.
Chapter - 6
Vegetative Propagation
Ex- F Answer the following questions:-
1. What is vegetative propagation?
Ans. Vegetative propagation is the process of obtaining new plants from stems, leaves and roots of a plant instead of seeds.
Ans. Vegetative propagation is the process of obtaining new plants from stems, leaves and roots of a plant instead of seeds.
2. Plants like fungi and ferns do not bear flowers. Then how do they reproduce?
Ans. Plants like fungi and ferns do not bear flowers. So they reproduce with the help of their spores.
3. Differentiate between complete and incomplete flower.
Ans. A flower which has all the four whorls or principal parts like sepal, petal, carpel and stamen are present is known as a complete flower. Examples : - China rose and mustard. Whereas, a flower in which any one or more whorls is missing is called an incomplete flower. Examples : - Date palm, mulberry tree.
4. Define pollination.
Ans. Pollination is defined as the process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma. Where anther is a male part and stigma is a female part of a flower.
Chapter - 5
Growth and Reproduction in Plants
Ex - F Answer the following questions:-
1. What is dispersal of seeds? Name a few agents which help in dispersal of seeds.
Ans.- Plants cannot move as they are fixed to the ground and can't take their seeds to other places. So the process by which seeds are scattered away from the parent plant is called dispersal of seeds.
Wind, water, animals and explosion are a few agents which help in dispersal of seeds.
2. Write down the stages involved in agriculture.
Ans.- The stages involved in agriculture are as follows:-
1. Ploughing,
2. Adding fertilizers,
3. Sowing,
4. Irrigation,
5. Protection of crops,
6. Harvesting.
3. Define Rabi and kharif crops with examples.
Ans.- Rabi crops, which are also known as winter crops, are the crops that are grown from November to April. Example: - wheat, pea, mustard.
Whereas, Kharif crops are also known as Summer crops, are the crops that are grown from June to October. Example: - rice, jowar, bajra, jute.
4. What is germination? What are the conditions required for germination?
Ans.- The process by which seeds change into baby plants is called germination.
Air, water and warmth are the essential conditions which are required for germination.
5. Plants grow from parts other than the seeds. Name the plant parts and give examples.
Ans.- Plant part. Examples
1. Stem cutting - Rose, Hibiscus
2. Root - Dahlia, Carrot
3. Leaves - Bryophyllum, Begonia
4. Underground stem - Onion, Ginger
5. Spores - Mushroom, Moulds
Chapter - 4
Growth and Reproduction in Plants
Ex - F Answer the following questions:-
1. What is dispersal of seeds? Name a few agents which help in dispersal of seeds.
Ans.- Plants cannot move as they are fixed to the ground and can't take their seeds to other places. So the process by which seeds are scattered away from the parent plant is called dispersal of seeds.
Wind, water, animals and explosion are a few agents which help in dispersal of seeds.
2. Write down the stages involved in agriculture.
Ans.- The stages involved in agriculture are as follows:-
1. Ploughing,
2. Adding fertilizers,
3. Sowing,
4. Irrigation,
5. Protection of crops,
6. Harvesting.
3. Define Rabi and kharif crops with examples.
Ans.- Rabi crops, which are also known as winter crops, are the crops that are grown from November to April. Example: - wheat, pea, mustard.
Whereas, Kharif crops are also known as Summer crops, are the crops that are grown from June to October. Example: - rice, jowar, bajra, jute.
4. What is germination? What are the conditions required for germination?
Ans.- The process by which seeds change into baby plants is called germination.
Air, water and warmth are the essential conditions which are required for germination.
5. Plants grow from parts other than the seeds. Name the plant parts and give examples.
Ans.- Plant part. Examples
1. Stem cutting - Rose, Hibiscus
2. Root - Dahlia, Carrot
3. Leaves - Bryophyllum, Begonia
4. Underground stem - Onion, Ginger
5. Spores - Mushroom, Moulds
Safety and First Aid
Answer the following questions:-
1) How will you put out fire caused by an electric spark?
Ans.- Fire caused by an electric spark should be put off with the help of sand. We should never throw water over it, because water is a good conductor of electricity and you may get shocked. For big fires, fire extinguisher can be used.
2) What first aid should be given in case of a snake bite?
Ans.- In case of a snake bite first aid should be given by following these steps: -
a) First step should be to stop the poison from spreading we have to remain still and calm as the snake poison directly effects the nervous system and leads to death.
b) To prevent the spreading of poison a tight bandage is tied a little above the bitten area.
c) Do not let the victim sleep.
d) Take the victim to the doctor immediately.
3) What should be done if a person swallows poison?
Ans.- If a person swallows poison we should try to induce vomiting by making the victim drink lots of luke warm, salty water. This way the poisonous substance swallowed can be thrown out of the body. The victim should be then rushed to the hospital immediately.
4) Give three rules to be followed while driving.
Ans.- Three rules to be followed while driving: -
a) We should follow traffic rules everywhere.
b) We should never exceed the speed limit while driving.
c) We should never use mobile phones while driving.
Answer the following questions:-
1) How will you put out fire caused by an electric spark?
Ans.- Fire caused by an electric spark should be put off with the help of sand. We should never throw water over it, because water is a good conductor of electricity and you may get shocked. For big fires, fire extinguisher can be used.
2) What first aid should be given in case of a snake bite?
Ans.- In case of a snake bite first aid should be given by following these steps: -
a) First step should be to stop the poison from spreading we have to remain still and calm as the snake poison directly effects the nervous system and leads to death.
b) To prevent the spreading of poison a tight bandage is tied a little above the bitten area.
c) Do not let the victim sleep.
d) Take the victim to the doctor immediately.
3) What should be done if a person swallows poison?
Ans.- If a person swallows poison we should try to induce vomiting by making the victim drink lots of luke warm, salty water. This way the poisonous substance swallowed can be thrown out of the body. The victim should be then rushed to the hospital immediately.
4) Give three rules to be followed while driving.
Ans.- Three rules to be followed while driving: -
a) We should follow traffic rules everywhere.
b) We should never exceed the speed limit while driving.
c) We should never use mobile phones while driving.
Chapter - 3
The Nervous System
Answer the following questions:-
1.) Define the nervous system. Name the various parts of the nervous system.
Ans.- The nervous system is defined as the system that controls all other systems of our body. It consists of nerves and fibers which send and receive messages from different body parts.
The various parts of nervous system are as follows: -
a) Brain
b) Spinal cord
c) Nerves (along with the five sense organs)
2.) Name the various parts of the brain. Give one function of each.
Ans. - The various parts of the brain are as follows: -
a) Cerebrum:- Its function is to control the working of sense organs of our body.
b) Cerebellum:- It maintains the balance and posture of our body.
c) Brain stem :- It is responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, digestion, controlling blood pressure and heart beat etc.
3) What are reflex actions? Give examples.
Ans.- A reflex action is a rapid automatic response generated by our body to a sudden change in the surrounding. It is controlled by the spinal cord.
Examples: -
a) On touching a hot object we immediately remove our hand from it.
b) On seeing a pizza for dinner, the secretion of saliva in our mouth.
4) Name three types of nerves. Give function of each.
Ans:- Three types of nerves and their functions are as follows: -
a) Sensory nerves: - They carry messages from various parts of the body to the brain or spinal cord.
b) Motor nerves: -These nerves carry messages away from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles where the action has to be taken.
c) Mixed nerves: -These nerves carry both the functions, they carry messages from the brain and bring back them to the brain.
5) Name the five sense organs. Give function of each.
Ans:-The five sense organs and their functions are as follows: -
a) Eyes: -They help us to see the wonderful things around us.
b) Ears: - They help us to hear voice around us.
c) Nose: - It helps us to smell different odours.
d) Tongue: - It helps us to sense a variety of tastes which include sweet, sour, salty and bitter. It also helps us to speak and swallow.
1.) Define the nervous system. Name the various parts of the nervous system.
Ans.- The nervous system is defined as the system that controls all other systems of our body. It consists of nerves and fibers which send and receive messages from different body parts.
The various parts of nervous system are as follows: -
a) Brain
b) Spinal cord
c) Nerves (along with the five sense organs)
2.) Name the various parts of the brain. Give one function of each.
Ans. - The various parts of the brain are as follows: -
a) Cerebrum:- Its function is to control the working of sense organs of our body.
b) Cerebellum:- It maintains the balance and posture of our body.
c) Brain stem :- It is responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, digestion, controlling blood pressure and heart beat etc.
3) What are reflex actions? Give examples.
Ans.- A reflex action is a rapid automatic response generated by our body to a sudden change in the surrounding. It is controlled by the spinal cord.
Examples: -
a) On touching a hot object we immediately remove our hand from it.
b) On seeing a pizza for dinner, the secretion of saliva in our mouth.
4) Name three types of nerves. Give function of each.
Ans:- Three types of nerves and their functions are as follows: -
a) Sensory nerves: - They carry messages from various parts of the body to the brain or spinal cord.
b) Motor nerves: -These nerves carry messages away from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles where the action has to be taken.
c) Mixed nerves: -These nerves carry both the functions, they carry messages from the brain and bring back them to the brain.
5) Name the five sense organs. Give function of each.
Ans:-The five sense organs and their functions are as follows: -
a) Eyes: -They help us to see the wonderful things around us.
b) Ears: - They help us to hear voice around us.
c) Nose: - It helps us to smell different odours.
d) Tongue: - It helps us to sense a variety of tastes which include sweet, sour, salty and bitter. It also helps us to speak and swallow.
Chapter - 2
The Circulatory System
Answer the following questions:-
1. Give three functions of blood.
Ans.- Three functions of blood are as follows: -
a) Blood transports nutrients and hormones from the alimentary canal to all parts of the body.
b) It helps in transporting oxygen from lungs to different parts of the body.
c) It carries carbon dioxide formed during respiration to the lungs for exhalation.
2. Define circulatory system.
Ans.- The circulatory system is defined as the system which helps in transporting nutrients and other useful substances from one part to the other part of the body.
3. What is blood?
Ans.- Blood is the red coloured liquid which helps in transporting nutrients and other substances to all parts of the body which consists of blood cells, plasma and platelets.
4. Why arteries have thick walls?
Ans.- Arteries have thick muscular walls because they have to distribute blood to all parts of body and blood in them rushes at high pressure.
5. What is double circulation?
Ans.- Double circulation is a process in which the blood has to pass twice through the heart making one complete round through the body.
Chapter- 1
The Skeletal System
Answer the following questions:-
1. What are vertebrae?
Ans.- The small bones that form the vertebral column are called vertebrae.
2. Give the functions of skeletal system.
Ans.- The functions of skeletal system are
I. Support : It provides structural support to the entire body.
II. Protection : It protects the delicate internal organs like heart and brain.
III. Movement : It helps in the movement of different parts of our body.
IV. Storage : The bones of the skeleton store minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
3. Which ribs are known as floating ribs?
Ans.- The last two pairs of ribs that are not attached to sternum are known as floating ribs.
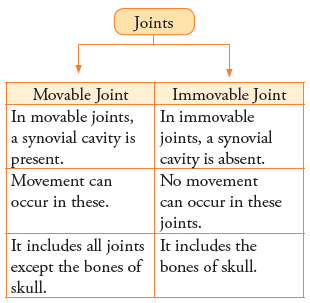
4. Differentiate between movable and immovable joints.
Ans.- Difference between movable and immovable joints are-
5. Give the Function of Cartilage.
Ans.- Function of Cartilage is to protect the bones from wear and tear and increase the life of bones.
Can you explain, why?
1. Our backbone is composed of 33 small irregular bones. What would happen if instead of these only one straight bone is present?
Ans.- The small 33 irregular bones at our backbone help us to bend and twist at wrist. If only one straight bone is present than we would not be able to bend and sit.
2. Sanjam’s friend is suffering from rickets. Doctor advised him to increase his intake of milk. Why?
Ans.- Rickets is the condition where the bones become brittle. Taking calcium rich food makes the bones strong. Milk is the rich source of calcium so, Doctor advised him to increase the intake of milk.