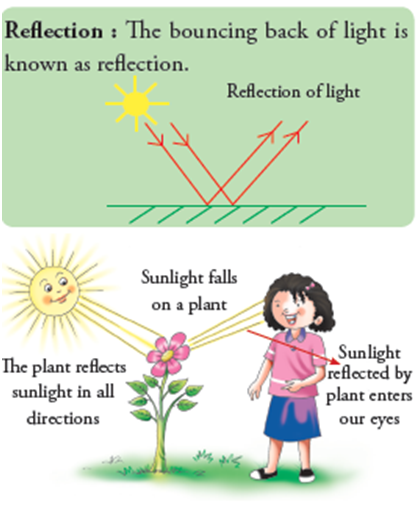
EFFECTS OF FORCE
TYPES OF FORCE

Screw
Screw has been derived from an inclined plane. It is like a nail with grooves cut in it. The grooves provided on the screw hold things tightly together which is why a screw is always better than the nail.
In the figure B, load is to
Pulleys are also used in cranes to lift loads.
Atom: The smallest particle of matter is known as atom.
Example: Gold, silver.
Molecule: Atoms of the same or different kind join together to form molecules.
Example: Oxygen, water.
Now watch this introduction video...
 There are three states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas. Let us study about the molecules and their arrangement.
There are three states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas. Let us study about the molecules and their arrangement.
Solids
Properties of Solid:
- Molecules are closely packed in solids.
- Solids have high density.
- They have definite volume.
Examples:
- Molecules are loosely packed in liquids.
- Liquids have medium density
- Liquids also have definite volume.
Examples:
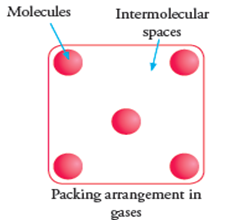
- Molecules are very loosely packed.
- Gases do not have fixed shape. They also take the shape of container.
- Gases do not have a definite volume.
- Gases have low density.
Examples:
There are three states of matter. Few substances like water can exist in more than one state. These states are brought about by application of heat.
Water exists in liquid state in ponds, wells, seas and ocean. When we heat water, it starts boiling and changes into gaseous state known as water vapours.
When we cool water it changes to solid state known as ice.
Freezing: The process in which liquid changes to solid on cooling is known as freezing
Example: Water to ice.
Example: Ice to water.
Example: Water to water vapours.
Example: Water vapours to water droplets.
A lever is a rigid rod which is free to move about a fixed point.
In this class, the fulcrum (F) lies in between the load (L) and the effort (E).
In this class, Load (L) lies in between Fulcrum (F) and Effort (E).
In this type, Effort (E) lies in between the Fulcrum (F) and the Load (L).
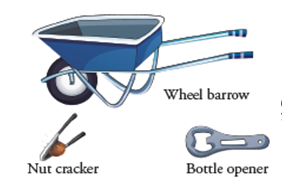
An inclined plane is a simple sloping surface which is used to push up objects instead of lifting them up. The ramp outside our houses is a perfect example of an inclined plane. Imagine how your father would have managed to bring the car inside your home if that ramp was not there. Would it be possible?
Wedge is a simple machine which works on the principle of an inclined plane. It has 2 inclined surfaces put together to have a sharp cutting edge.
For example: Knife, a needle, an axe which we see around us in our daily life are all wedges. The sharp ‘V’ formed due to joining of two inclined planes is used
to force things apart.
Screw has been derived from an inclined plane. It is like a nail with grooves cut in it. The grooves provided on the screw hold things tightly together which is why a screw is always better than the nail.
A pulley is a simple machine which is used to lift heavy loads very easily. It changes the direction of force and hence makes it easy to lift heavy loads. It is difficult to lift because it is against the force of gravity. It is easy to drop because it works in the direction of force of gravity.
A simple fixed pulley consists of a wheel with a groove and having a rope wound around it.
Can you imagine a car without wheels or your bicycle without wheels?
The wheel and axle is a simple machine in which a wheel is attached to a cylindrical rod called axle or the wheel rolls upon the axle.
To make these machines work for a longer time we should keep in mind the following points:
1. Since most of the parts are made of iron, therefore, they must be painted against rusting.
2. Machines should be lubricated because there takes place a lot of wear and tear due to frictional forces.
3. Machines should be kept covered when not in use.
Work is said to be done when an applied force m
- A force should be applied on the body.
- The force applied should move the body.
When you learn your lesson, mental work is said to be done.
Energy is the ability to do work. We get energy from food we eat. This energy gets stored in our body and helps us to do work.
Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can be converted from one form to the other.
Sun is the main source of energy on earth. Sun’s energy is taken by green plants to prepare their food. The green plants are eaten by herbivores and energy gets transferred to their body. Herbivores are further eaten by carnivores and the energy is further transferred to carnivores.
The energy possessed by a body due to its state of rest or of motion is known as mechanical energy.
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion is known as kinetic energy.
Example : The water flowing in a river possess kinetic energy.
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its state of rest is known as potential energy.
Example : A stone lying at a height possess potential energy.
It is the energy stored in the molecules of some chemicals.
Example: Matchstick, wood and coal.
(i) Contact Forces
(ii) Non-Contact Forces
(i) Contact Forces : The forces which act when two bodies touch each other are known as contact forces.
Example : Frictional force.
(ii) Non-Contact Forces : The forces which act when two bodies do not touch each other are known as non-contact forces.Example : Magnetic force.
The total force acting on a body is called net force or resultant force.
If the force is acting in one direction, then the resultant force is sum of all the forces.
Work is said to be done when an applied force moves the body through some distance.
Work = Force × Distance
Unit of Work
Work done is measured in Joules (J).
- A force should be applied on the body.
- The force applied should move the body.
ENERGY
Energy is the ability to do work. We get energy from food we eat. This energy gets stored in our body and helps us to do work.
Principle of Energy Conservation
Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can be converted from one form to the other.
Main Source of Energy
Sun is the main source of energy on earth. Sun’s energy is taken by green plants to prepare their food. The green plants are eaten by herbivores and energy gets transferred to their body. Herbivores are further eaten by carnivores and the energy is further transferred to carnivores.
The energy possessed by a body due to its state of rest or of motion is known as mechanical energy.
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion is known as kinetic energy.
Example : The water flowing in a river possess kinetic energy.
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its state of rest is known as potential energy.
Example : A stone lying at a height possess potential energy.
It is the energy stored in the molecules of some chemicals.
Example: Matchstick, wood and coal.
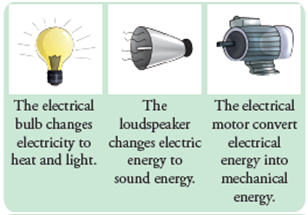
The energy possessed by a magnet is known as magnetic energy.
The objects which allow light to pass through it are known as transparent objects.
Example : Ordinary glass.
Translucent
The objects which allow partial amount of light to pass through it are known as translucent objects.
Example : Butter paper.
Opaque
The objects which do not allow light to pass through it are known as opaque objects.
Example : Wood, concrete wall.
(ii) for construction of buildings.
(iii) for making toys, pots and decorative articles.
Methods to Conserve Soil
Q.1. Write five methods of soil conservation.

Now watch this introduction video...
MOLECULES AND THEIR ARRANGEMENT
 There are three states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas. Let us study about the molecules and their arrangement.
There are three states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas. Let us study about the molecules and their arrangement.
Solids
Properties of Solid:
- Molecules are closely packed in solids.
- Solids have high density.
- They have definite volume.
Examples:
- Molecules are loosely packed in liquids.
- Liquids also have definite volume.
Examples:
Properties of Gas:
- Molecules are very loosely packed.
- Gases have low density.
Examples:
There are three states of matter. Few substances like water can exist in more than one state. These states are brought about by application of heat.
Water exists in liquid state in ponds, wells, seas and ocean. When we heat water, it starts boiling and changes into gaseous state known as water vapours.
When we cool water it changes to solid state known as ice.
Freezing: The process in which liquid changes to solid on cooling is known as freezing
Example: Water to ice.
Example: Ice to water.
Carrot and sweet potato can grow into new plants from their roots.
Some plants like fern and fungi do not bear flowers. They produce their spores, each of which grows into a new plant.
A flower in which all the four whorls i.e., sepal, petal, stamen and carpel are present is known as a complete flower.
Example : China rose and mustard. Incomplete Flower
A flower in which one or more whorls is missing is called an incomplete flower.
Example : Date palm and mulberry tree.
Functions of Flowers:
1. Many flowers produce sweet, sticky substance called nectar.
2. Many flowers like rose and jasmine produce perfume.
3. Spices are the dried flower buds.
4. Flowers help in the process of reproduction. Pollination
The process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination.
(i) Ovary develops to form the fruit.
(ii) Ovules present in the ovary form the seeds.
- Never use mobile phones while driving.
- Always use an indicator to change the lane.
- On a two wheeler both the riders should wear a helmet.
- Children should not be given scooter or cars for driving before the age of 18.
- Always be careful while crossing an unmanned railway crossing.
Safety in case of fire is very essential because a single spark may lead to a big and harmful fire accident. Fire accidents are generally caused by electric sparks, smoking, leakage of cooking gas or petrol, fire crackers etc. Rules that should be followed for fire safety.
you may get shock.
- If possible cooking gas cylinders should be kept in the open and the supply pipe should be changed regularly.
- Always wear cotton clothes while cooking. Never wear nylon clothes because they catch fire easily.
- Fire caused due to petrol should always be put out by throwing sand or fire extinguisher.
This is because petrol is lighter than water and hence floats on water and continues to get air supply. The fire doesn’t get extinguished.
Injury
- The victim should not be surrounded by too many people and should be given mental calm.
- Next step is to give immediate medical help.
- The type of help to be given depends on the type of injury.
Cuts and Wounds
Cuts and wounds expose the internal tissues to the air that contains germs and dust. This may cause infection if proper care is not taken.
- Always clean the wound with an antiseptic solution like dettol that kills germs and then apply some antiseptic cream.
- Don’t let flies sit on the wound.
• In case of bleeding:
- Use an ice pack (crushed ice in a thick towel) to stop bleeding.
- Tie a tight band above the wound for stopping the
Burns
When the skin gets exposed to high temperature, the outer layer of the skin gets removed and exposes the inner sensitive layers to germs and dust.
- In case of a burn, immediately wash the burnt part with cold water.
- Apply an antiseptic like burnol to the wound.
- If antiseptic is not available use a mixture of baking soda and water to the burnt area.
Similarly, nutrition and digestion processes are of no value unless and until the digested food or nutrients are transported from the alimentary canal to all body cells, where these are actually needed and utilized. Hence, all higher organisms need such a pipeline system to transport nutrients which is known as circulatory system.
Thus, “the system which helps in transporting nutrients and other substances from one part of the body to the other part of the body is known as circulatory system”.
In animals, it consists mainly of three parts.(i) Blood
(ii) Heart
(iii) Blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries)
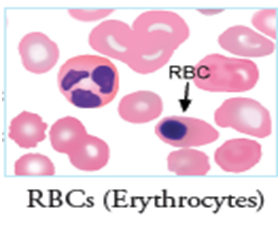
BLOOD
3. It takes carbon dioxide formed during respiration to lungs for exhalation.
4. It helps in transportation of hormones.
5. It transports heat and hence maintain constant temperature of the body.
6. It maintains water level in the body.
7. It helps in the removal of waste material from the body.
Differences between Artery and Vein
Artery
- Arteries are deep seated.
- Arteries pump blood from heart to various parts of the body.
- Arteries have thick walls.
- Arteries mostly carry oxygenated blood.
Vein
- Veins are superficial.
- Veins collect blood from various parts of the body and take it to heart.
- Veins have thin walls.
- Veins mostly carry deoxygenated blood.
THE HEART
The heart of man is reddish brown in colour. It is the main pumping organ of the body. It pumps and collects blood to and from various body parts. It is of the size of a human closed fist.
It is located between the two lungs well protected by lungs. The broad portion of heart is upwards and apex points downward.
- Lungs enrich the blood with oxygen. This oxygenated blood is poured into left auricle.
- From left auricle, the blood is pumped into left ventricle.
- From left ventricle it is pumped to all parts of body.
- The impure blood is collected and poured into right auricle.
- Right auricles pump it into right ventricle.
- Right ventricle pumps it to lungs for oxygenation. This entire circle repeats itself.
The human body is the most complex of all organisms present on this earth. A human body is made-up of nearly 206 bones.The skeletal system is a system which supports the framework of bones in our body and gives it a particular and definite shape.
The human skeleton consists of the skull, the backbone, the ribcage and two pairs of limbs.
 Skull : Acts like a helmet and protects the brain.
Skull : Acts like a helmet and protects the brain.
Forelimbs : Help us to lift various objects.
Ribcage : Protects delicate organs like heart and lungs.
Lower Limbs : Along with muscles they help in movement.
The framework of bones present in our body is known as skeleton.
Bone
Bones are made-up of minerals which include calcium and phosphorus. These make the bones strong.
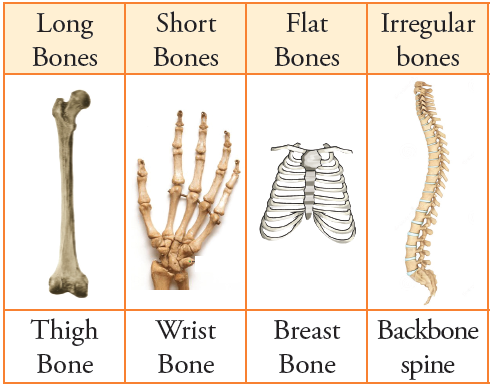
Types of Bones
Bones may be short, long, flat or irregular.
 Skull
Skull
The skull protects the brain. It is a hollow round structure present in the head.

 Functions :
Functions :
1 The skull covers and protects the brain.
2 It gives shape to the face.
3 It supports the teeth present in upper and lower jaw.
 NOTE : All the bones that form the skull are fixed and immovable, except for the lower jaw.
NOTE : All the bones that form the skull are fixed and immovable, except for the lower jaw.
Backbone
The bone present on the extreme back of our body is known as backbone. It is also known as the vertebral column or spine. The skull is attached to the backbone.
 Vertebral Column — Long bony structure made-up of 33 bones.
Vertebral Column — Long bony structure made-up of 33 bones.
Vertebra : The small bones that form the vertebral column are called vertebrae.
Function : The backbone encloses and protects the delicate spinal cord.
Ribcage
The bony cage present in the chest region is called the ribcage. It is made-up of 12 pairs of thin curved bones called ribs.
 Sternum : The long flat bone present in the centre of chest is called sternum.
Sternum : The long flat bone present in the centre of chest is called sternum.
Backbone : The bone present at the back supporting the ribs is known as backbone. Now watch this video to help you understand the chapter better.Assignment : -1.) Draw "The Skeletal System" given on page no. - 6 in your OCBs.
The human skeleton consists of the skull, the backbone, the ribcage and two pairs of limbs.

Forelimbs : Help us to lift various objects.
Ribcage : Protects delicate organs like heart and lungs.
Lower Limbs : Along with muscles they help in movement.
The framework of bones present in our body is known as skeleton.
Bone
Bones are made-up of minerals which include calcium and phosphorus. These make the bones strong.
Types of Bones
Bones may be short, long, flat or irregular.


The skull protects the brain. It is a hollow round structure present in the head.


1 The skull covers and protects the brain.
2 It gives shape to the face.
3 It supports the teeth present in upper and lower jaw.

Backbone
The bone present on the extreme back of our body is known as backbone. It is also known as the vertebral column or spine. The skull is attached to the backbone.

Vertebra : The small bones that form the vertebral column are called vertebrae.
Function : The backbone encloses and protects the delicate spinal cord.
Ribcage
The bony cage present in the chest region is called the ribcage. It is made-up of 12 pairs of thin curved bones called ribs.

Backbone : The bone present at the back supporting the ribs is known as backbone.
ReplyForward |